http://wiki.answers.com
Cable, dial-up, satellite, mobile (EDGE, 3G, etc.), DSL.
As technology grows, so does our need for things to go faster. Ten years
ago, websites just included images, coloured text and some repetitive
melodies. Now Flash websites, animations, high resolution photos, online
gaming, videos or streaming ( radio on the internet ), are getting more
popular for people who demand faster and faster internet connections.
The connection speeds listed below represent an average speed at the
time of publication ( May 2009 ). This will no doubt change over time.
1)
CABLE:
http://en.wikipedia.org
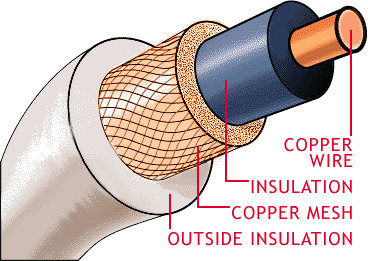
A cable is most often two or more wires running side by side and bonded, twisted or braided together to form a single assembly, but can also refer to a heavy strong rope. In mechanics cables, otherwise known as wire ropes, are used for lifting, hauling and towing or conveying force through tension. In electrical engineering cables are used to carry electric currents. An optical cable contains one or more optical fibers in a protective jacket that supports the fibers.



PCL:
http://www.petervaldivia.com
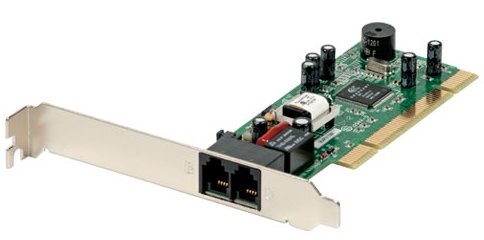
2) PCI modem( see image above ). Analogue up to 56000 bits per second. It means that in a second, 56000 bits ( 0 or 1 ) travel through the copper wire. It is both economical and slow and it is also called dial-up access. If you connect the modem, you get internet but as it uses the analogue telephone line, if you surf on the internet, nobody can call you because the line is busy.
Using a modem connected to your PC which is very cheap ( about 10 €) , users connect to the Internet only if you click on the telephone Access Icon and the computer dials the phone number provided by your ISP ( Internet Service Provider ) and connects to the network. The signal is analogue because data is sent over an analogue telephone network. This modem converts received analogue data to digital ( always analogue on the telephone site and digital on the computer side ).
As dial-up access uses ordinary telephone lines the data rates are limited and the quality of the connection is not always good. Nowadays very few people use this type of connection.
SATELLITE:
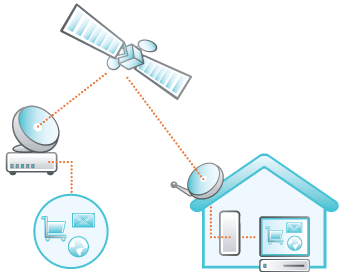
3) Satellite
IoS
short for Internet over Satellite allows a user to access the
Internet via a geostationary satellite that orbits the earth. A
geostationary satellite is a type of satellite placed at a fixed
position above the earth's surface. Because of the large distances
between home and satellite, signals must travel from the earth up
to the satellite and back again. It causes a slight delay between
the request and the answer.
http://www.answers.com
http://www.webopedia.com
While technology changes at a rapid pace, so do Internet
connections. The connection speeds listed below is a general snapshot,
representing general average to maximum speeds at the time of
publication.
As technology grows, so does our need for bigger, better and
faster Internet connections. Over the years the way content is presented
via the Web
has also changed drastically.Ten years ago being able to center, bold,
and produce text in different colors on a webpage was something to
admire. Today, Flash, animations, online gaming, streaming HD video,
database-driven websites, ecommerce and mobile applications—to name but a
few—are standards.The need for speed has changed the options available to consumers and businesses alike in terms of how and how fast we can connect to the Internet. The connection speeds listed below represent a snapshot of general average to maximum speeds at the time of publication. This is no doubt will change over time and Internet connection speeds also vary between Internet Service Providers (ISP)


Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento